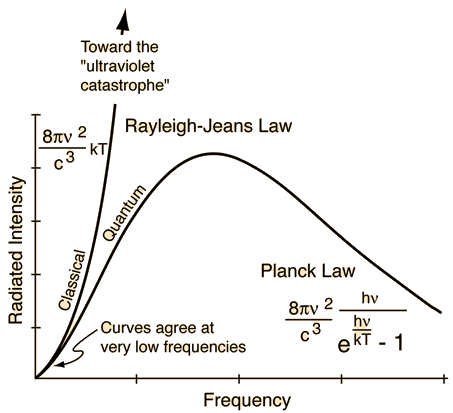
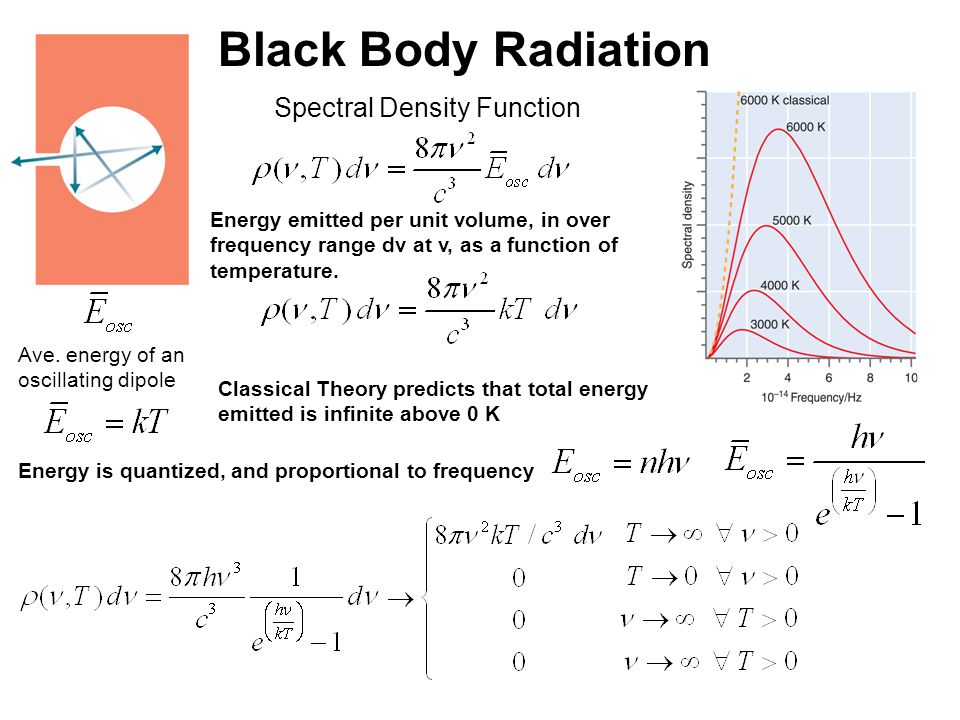
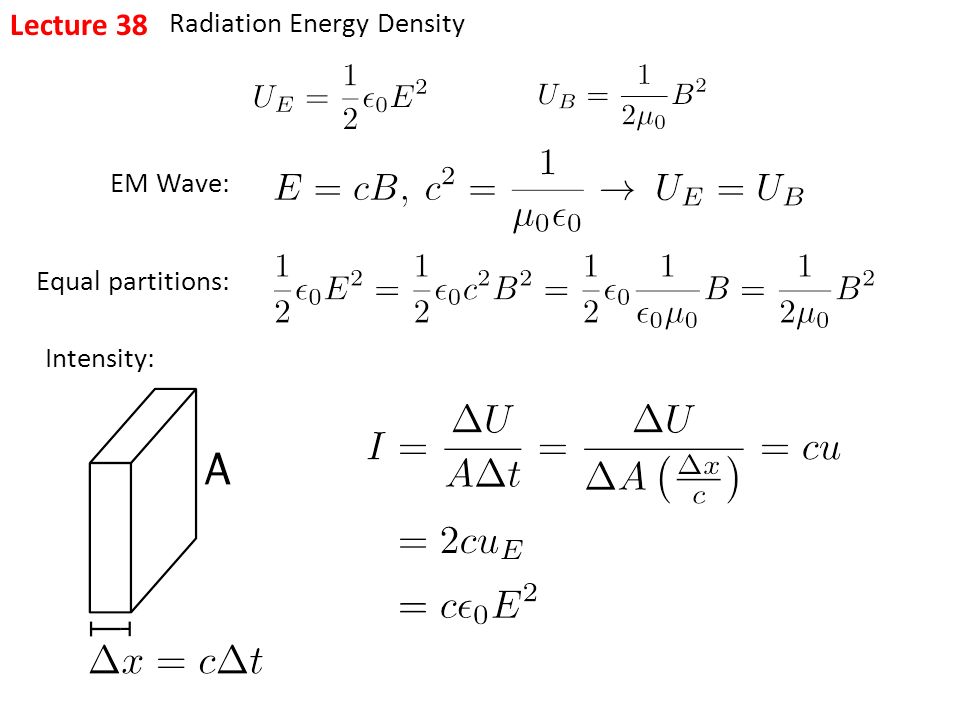
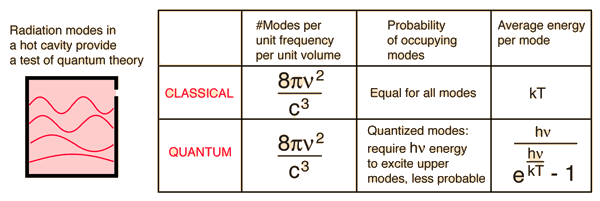
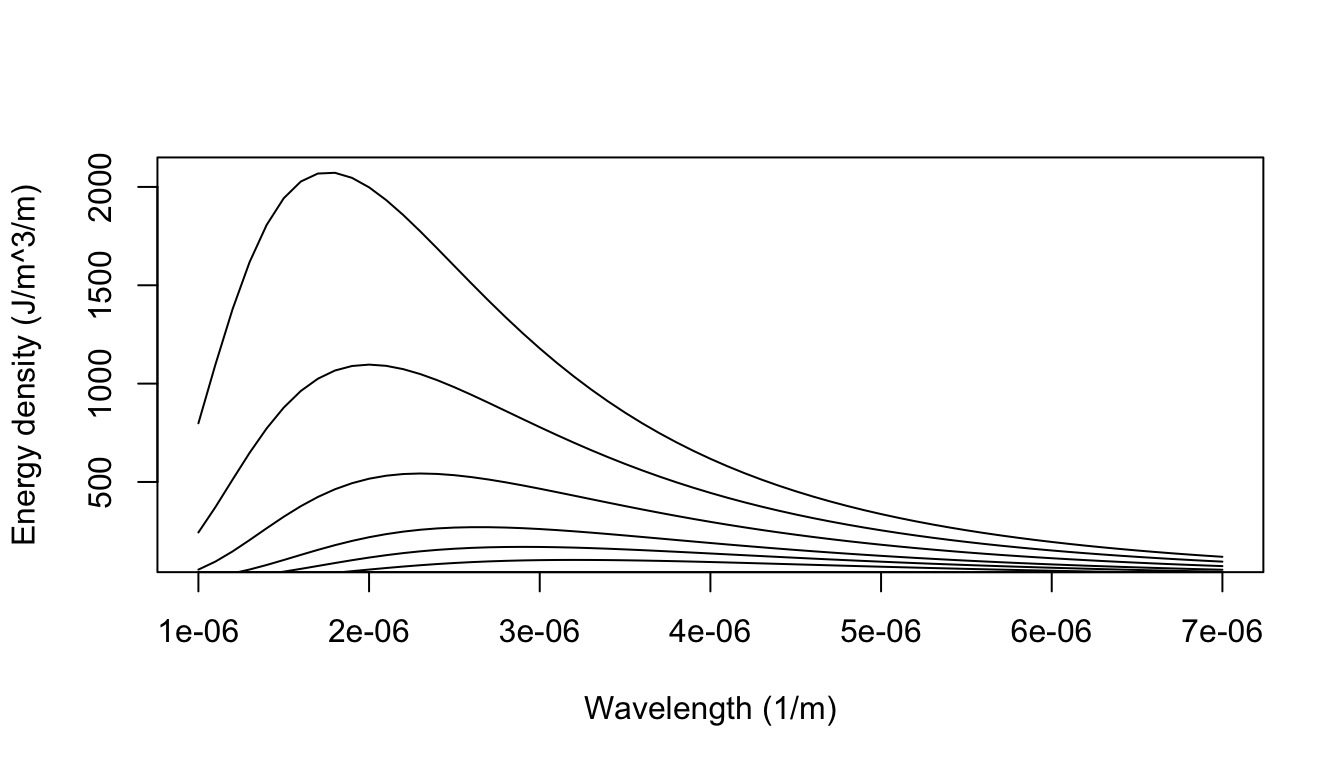
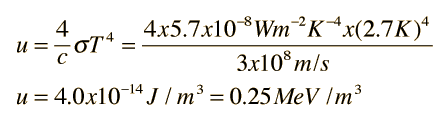The radiation energy density per unit wavelength at a temperature T has a maximum at a wavelength lambda(0). At temperature 2T, it will have a maximum wavelength

The radiation energy density per unit wavelength at a temperature T has a maximum at a wavelength lambda(0). At temperature 2T, it will have a maximum wavelength

Spectral energy density of blackbody radiation at different temperatures. | Download Scientific Diagram